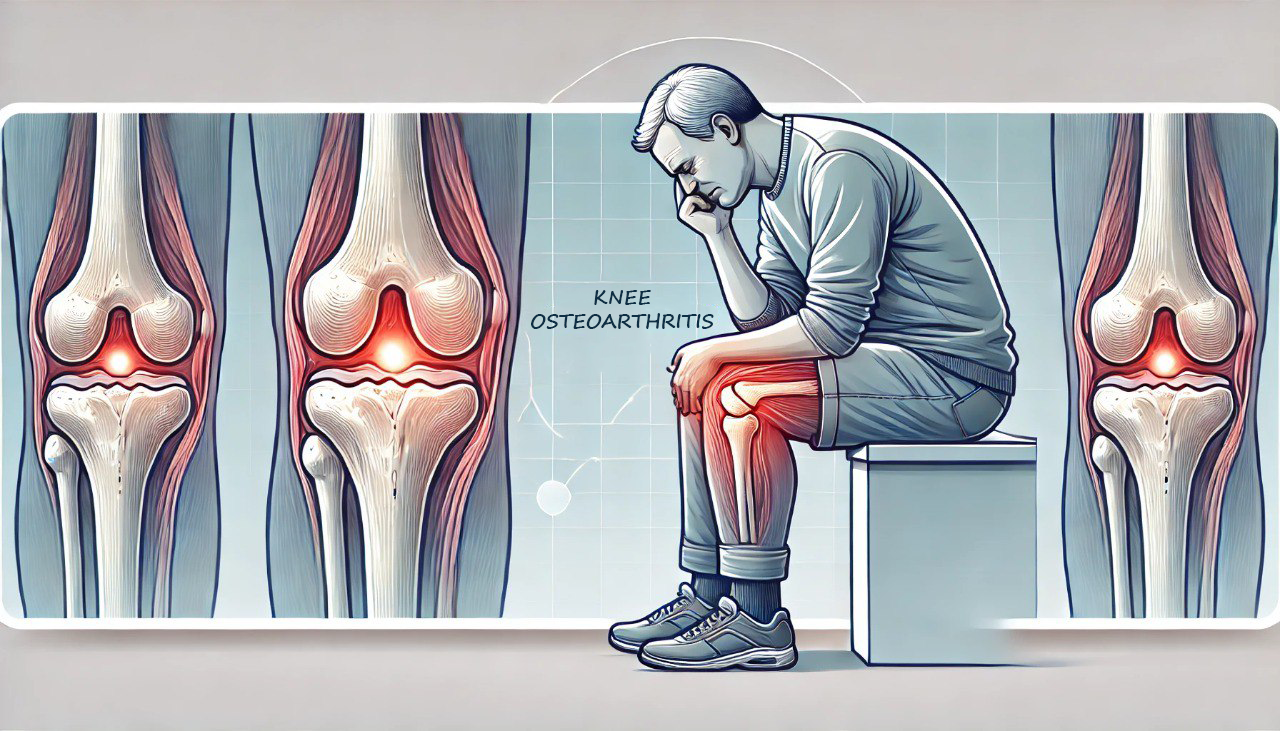
Definition of Knee Osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis results from a fundamental biological process that disrupts the balance between the synthesis and degradation of cartilage and subchondral bone.
Various factors, including genetic, developmental, metabolic, and traumatic influences, can initiate this imbalance.
Consequently, the final manifestation of osteoarthritis involves a range of changes: morphological, biochemical, molecular, and biomechanical alterations in both the cells and matrix of the cartilage.
These changes ultimately lead to degeneration, fissures, and loss of articular cartilage, as well as subchondral sclerosis, osteophyte formation, and damage to the subchondral cartilage.
Nguyên nhân
- Thoái hóa khớp nguyên phát
Là nguyên nhân chính, xuất hiện muộn, thường ở người sau 60 tuổi, có thể ở một hoặc nhiều khớp, tiến triển chậm. Ngoài ra có thể có yếu tố di truyền, yếu tố nội tiết và chuyển hoá (mãn kinh, đái tháo đường...) có thể gia tăng tình trạng thoái hóa.
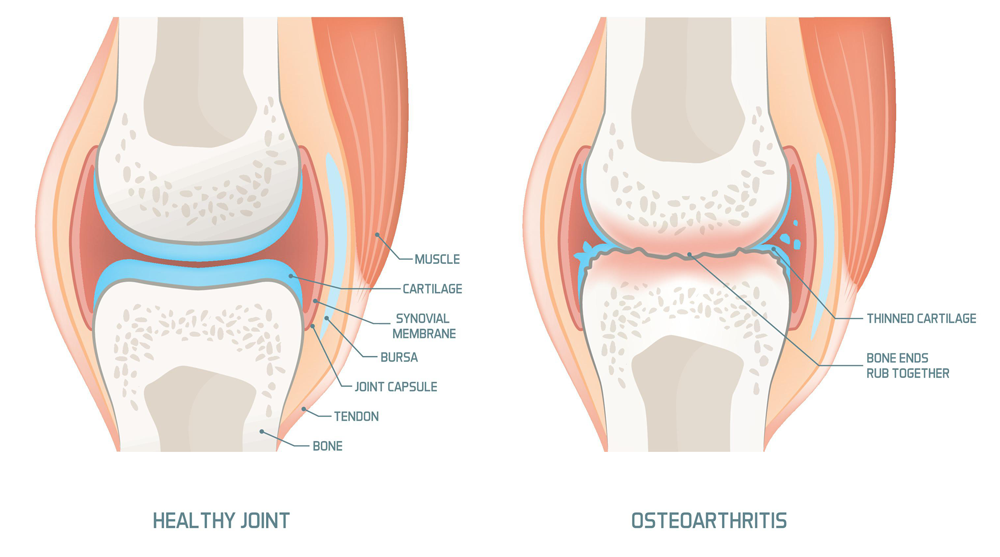
- Thoái hoá khớp thứ phát
Bệnh gặp ở mọi lứa tuổi, nguyên nhân có thể do:- Sau các chấn thương khiến trục khớp thay đổi (gãy xương khớp, can lệch...)
- Các bất thường trục khớp gối bẩm sinh: khớp gối quay ra ngoài (genu valgum); khớp gối quay vào trong (genu varum); khớp gối quá duỗi (genu recurvatum...)
- Sau các tổn thương viêm khác tại khớp gối (viêm khớp dạng thấp, bệnh gút)
Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis
- Đau quanh khớp gối là triệu chứng đặc trưng, tùy đợt cấp hay mạn tính mà có thể đau dữ dội hoặc âm ỉ. Đau tăng khi đi đứng, giảm khỉ nghỉ ngơi.
- Hạn chế vận động của khớp gối, giảm biên độ gập của gối.
- Lạo xạo gối khi co duỗi.
- Khớp gối biến dạng, lệch trục.
- Dễ mỏi khi đi đứng lâu.
- Khớp gối có thể sưng.
Chẩn đoán
Áp dụng tiêu chuẩn chẩn đoán của Hội thấp khớp học Mỹ-ACR (American College of Rheumatology), 1991.
Các cận lâm sàng hỗ trợ chẩn đoán và điều trị:
- Xquang khớp gối: hình ảnh gai xương, hẹp khe khớp, tăng sản đầu xương.
- Siêu âm khớp gối: đánh giá tình trạng hẹp khe khớp, gai xương, tràn dịch khớp, đo độ dày sụn khớp, màng hoạt dịch khớp, phát hiện các mảnh sụn thoái hóa bong vào trong ổ khớp.
- Chụp cộng hưởng từ (MRI): phương pháp này có thể quan sát được hình ảnh khớp một cách đầy đủ trong không gian ba chiều, phát hiện được các tổn thương sụn khớp, dây chằng, màng hoạt dịch.
- Nội soi khớp gối: phương pháp nội soi khớp quan sát trực tiếp được các tổn thương thoái hoá của sụn khớp ở các mức độ khác nhau (theo Outbright chia bốn độ), qua nội soi khớp kết hợp sinh thiết màng hoạt dịch để làm xét nghiệm tế bào chẩn đoán phân biệt với các bệnh lý khớp khác.
- Xét nghiệm máu và sinh hoá: Tốc độ lắng máu bình thường.
Chẩn đoán phân biệt
- Viêm khớp dạng thấp: chẩn đoán phân biệt khi chỉ tổn thương tại khớp gối, đặc biệt khi chỉ biểu hiện ở một khớp: tình trạng viêm tại khớp và các biểu hiện viêm sinh học rõ (tốc độ máu lắng tăng, CRP tăng…) và có thể có yếu tố dạng thấp dương tính. Thường được chẩn đoán qua nội soi và sinh thiết màng hoạt dịch.
- Viêm khớp gút: đợt cấp của viêm khớp gút và thoái hóa khớp có thể có triệu chứng giống nhau, cần phân biệt rõ để tránh nhầm lẫn và điều trị đúng.

Điều trị
- Nguyên tắc điều trị
- To manage knee osteoarthritis effectively, focus on pain relief during progression.
- Additionally, aim to restore joint mobility and limit or prevent joint deformities.
- Moreover, be cautious to avoid unwanted drug side effects, paying attention to drug interactions and associated diseases, particularly in the elderly.
- Ultimately, improving the quality of life for patients remains a key goal.
- Điều trị không dùng thuốc
- Change your lifestyle by avoiding standing or sitting for prolonged periods. Moreover, exercise moderately and appropriately to maintain joint health.
- In addition, acupuncture can significantly improve symptoms such as pain, weakness, and knee fatigue.
- Similarly, acupressure massage helps relieve pain, relax muscles, and enhance circulation in the knee area.
- Furthermore, physical therapy methods like electrotherapy, ultrasound, and infrared therapy are highly effective for managing knee osteoarthritis.
- Điều trị dùng thuốc
- Pain relief options include: Paracetamol and Tramadol.
- Additionally, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as Celecoxib and Piroxicam can be used.
- In contrast, topical anti-inflammatory drugs generally have fewer side effects compared to oral medications.
- Moreover, corticosteroids are not indicated for systemic use.
- For intra-articular injections, options include Hydrocortisone acetate, Hyaluronic acid (AH) in the form of hyaluronate, Betamethasone, and Methylprednisolone.
- Furthermore, slow-acting anti-degenerative drugs such as Piascledine and Glucosamine sulfate are available.
- Autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatment involves taking venous blood, adding an anticoagulant, centrifuging to separate plasma, and then injecting 6ml-8ml of PRP into the knee joint.
- Additionally, stem cell transplantation uses stem cells extracted from autologous adipose tissue (Adipose-derived Stem-Cell-ADSCs) or autologous bone marrow.
- Điều trị ngoại khoa
- Arthroscopic treatment options include debridement, shaving, and joint lavage. Additionally, drilling to stimulate bone formation (known as microfracture) and cartilage cell transplantation are used to address cartilage damage.
- On the other hand, artificial joint replacement surgery is typically indicated in severe, progressive cases where there is significant loss of motor function. This procedure is usually applied to patients over 60 years old and may involve partial or total knee replacement.
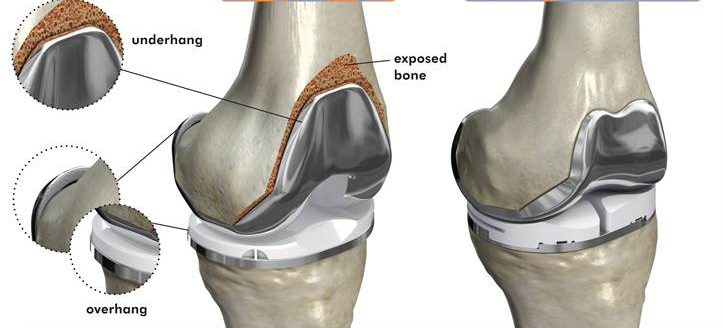
Phòng ngừa
To prevent knee osteoarthritis, it is essential to maintain a healthy weight and prevent obesity. Additionally, having a reasonable exercise regimen can help protect joints from overload and reduce the risk of developing the condition. Moreover, early detection and treatment of orthopedic joint deformities, such as joint misalignment or knee joint curvature (internal or external), are crucial for preventing the progression of knee osteoarthritis.