Definition of Tension headaches
Đau đầu căng thẳng là loại đau đầu phổ biến nhất, rất thường gặp. Hầu hết ai trong chúng ta cũng từng gặp ít nhất một lần trong đời.
Although not a dangerous acute disease, tension headaches significantly affect our lives and activities, especially if not treated properly, it can lead to chronic headaches that are very difficult to treat.
Causes of Tension headaches
The muscles of the head, face, and neck can constrict due to depression, anxiety, stress, sitting for long periods, or trauma.
In addition, there are some risk factors such as insomnia or sleeping too much, overeating, alcohol and stimulant use, noisy working environment, family and social stress.

When these muscles constrict, they cause pain by increasing pressure on the scalp and neck muscles. Consequently, the reduced blood supply leads to anemia, which prompts the muscles to produce lactic acid. This, in turn, stimulates the release of pain-causing substances.
Symptoms of Tension headaches
Tension headaches often have the following symptoms:
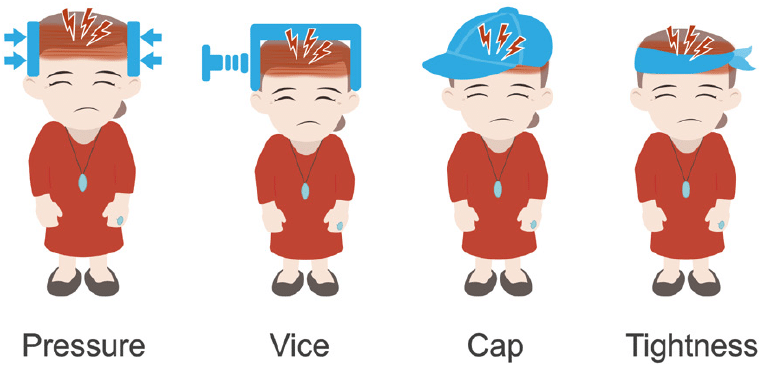
- The headache can last from a few minutes to several days.
- The pain typically feels like squeezing or heaviness on one or both sides of the head.
- Pain intensity ranges from mild to moderate to severe.
- During an episode, a pulsing sensation may be noticeable.
- The pain may worsen with movement or in noisy environments.
- Dizziness may also accompany the pain.
The above symptoms often cause discomfort and affect the patient’s daily life and work, so diagnosis and treatment are urgent and necessary.
Chẩn đoán
Diagnosis of tension headache based on symptoms and the circumstances of the onset of the pain is necessary to exclude other secondary headache diseases. When necessary, it is possible to combine appropriate paraclinical tests:
- Head X-ray: a brief examination of bone and brain structures.
- Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): a comprehensive examination of brain structures.
- Blood tests: exclude systemic inflammatory diseases, tuberculosis
Chẩn đoán phân biệt:
- Migraine headache
- Cluster headache
- Secondary headache due to other causes: stroke, meningitis, menstrual-related headache.
Điều trị
After being diagnosed with tension headache, the patient needs appropriate treatment to improve symptoms as well as daily activities and work, avoiding progression to chronic tension headache, which is very difficult to treat.
Các phương pháp điều trị không dùng thuốc:
- Change your lifestyle to reduce symptoms: rest in a dark and quiet room, listen to relaxing music
- Avoid foods such as alcohol, beer, cigarettes, coffee, tea
- Regular exercise is recommended to increase body flexibility and muscle circulation.
- Maintain proper sleep hygiene and avoid overwork, stress, and pressure.
- Massage and acupressure on the head, face, and neck to help relax, reduce pain, and increase muscle circulation.
- Acupuncture helps relieve pain and relax muscles effectively.
- Physical therapy: music therapy, aromatherapy, hot/cold compresses, and electric shock effectively reduce headaches.

Drug treatment: treatment to stop and prevent attacks.
- Medication to relieve attacks: use common painkillers: Paracetamol/codeine/tramadol.
- Medication to prevent attacks: amitriptyline, mirtazapine, venlafaxine.
Phòng ngừa
Tension headaches are a disease that anyone can get at some point. Still, we can completely prevent with the following minor changes:
- Avoid stress in life, and have a reasonable living and working schedule.
- Exercise moderately to improve health.
- Avoid prolonged bad postures at work and study.
- Relax and rest properly after stressful working hours.
- Avoid abusing stimulants such as tea, coffee, alcohol, beer, and cigarettes.