Introduction
Nowadays, with the nature of office work, more and more people experience conditions such as wrist pain, hand numbness, reduced or lost sensation in the hand, etc. The above signs suggest Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Definition
Carpal tunnel syndrome: CTS is a pathology of the median nerve being compressed in the carpal tunnel; this is the most common syndrome among peripheral nerve compression diseases.
The pathophysiology is not clearly understood, but it may be due to the mechanism of increased pressure in the carpal tunnel causing disturbances in the microvascular supply in the outer and inner sheaths, thereby causing symptoms of damage to the median nerve.
Causes
Most carpal tunnel syndrome, also known as idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome, is primary.
Secondary carpal tunnel syndrome is often caused by the following: Carpal tunnel space-occupying mass, trauma, infection, joint disease, endocrine disease, obesity, etc.
Risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome include female gender, pregnancy, and occupations that use hands a lot.
Symptom
Patients often feel numbness, paresthesia like ants crawling, sharp pain like needles, or burning pain in the skin area under the control of the median nerve in the hand (thumb, index finger, middle finger, and half of the ring finger), and sometimes the whole hand. In the early stages, the above symptoms are often only encountered when using the hand and wrist for a long time, such as driving a motorbike, holding objects for a long time, using a computer a lot, etc., or at night due to peripheral venous congestion.
Motor disturbances of the median nerve in carpal tunnel syndrome are less common than sensory disturbances and often occur in the late stages of the disease. Patients usually describe the hand becoming weaker and more clumsy, having difficulty buttoning a shirt, or dropping objects when holding them.
Diagnosis
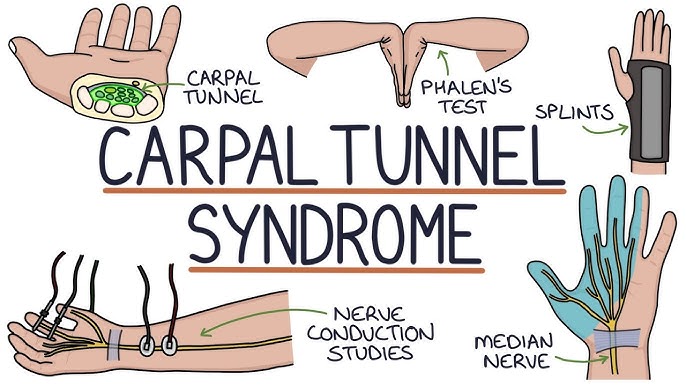
To diagnose whether a patient has carpal tunnel syndrome, the doctor needs to carefully exploit the patient’s functional and physical symptoms and combine paraclinical tests in his diagnosis to distinguish it from other clinical situations.
- Functional symptoms include symptoms of sensation in the skin area controlled by the median nerve in the hand: pain, numbness, paresthesia, tingling, ants crawling
- Physical symptoms include a positive Tinel’s sign, a positive Phalen’s test, and reduced or lost superficial sensation in the skin area controlled by the median nerve or nerve conduction test, showing dysfunction of the median nerve in the wrist area.
- AND evidence of risk factors-related medical history before the symptoms of CTS appear.
Paraclinical tests commonly used to support diagnosis and treatment include:
- Wrist X-ray: often used to assess the structure of the wrist bone and exclude lesions.
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist (MRI): can see soft tissue injuries, stenosis, and damage to the fibrous sheath.
- Electromyography (EMG): assesses the extent of damage to the nerve axons and predicts the recovery of the disease.
- Wrist ultrasound: Assesses the damage to the median nerve based on the cross-sectional area size on ultrasound.
- Blood test: often used to rule out systemic inflammatory diseases, tuberculosis, tumors, etc.
It is necessary to differentiate between primary and secondary carpal tunnel syndrome or neurological and musculoskeletal diseases in the upper limbs.
Treatment
If not diagnosed and treated promptly, it can lead to the most severe condition of loss of sensation and motor function of the hand.
- Non-drug treatment
- Patients must change their lifestyle and activities: relax the wrist and hand when working, practice proper wrist movements, avoid bad postures such as sleeping on the hand or bending the wrist, etc.
- Fix the wrist with a splint to reduce pressure.
- Stabilize underlying diseases to avoid secondary carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Physical therapy methods: electrotherapy, ultrasound therapy, cold/hot compresses.
- Traditional acupuncture methods have been proven to be more effective in prolonging and reducing pain than simple treatments.
- Acupressure massage helps release pressure on the wrist area and increases nutrition to the hand, thereby helping to reduce symptoms of pain and numbness.
- Drug treatment
- Step-by-step pain relievers such as Paracetamol/Codeine.
- NSAID anti-inflammatory pain relievers (Meloxicam, Diclofenac)
- Neuropathic pain relievers (Gabapentin, vitamin 3B)
- Corticosteroid injection into the carpal tunnel
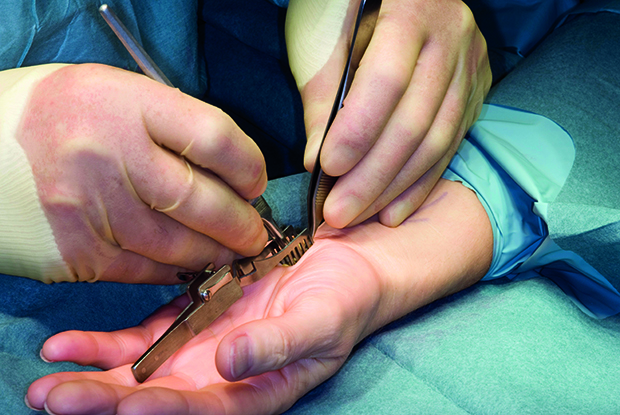
- Surgical treatment
- Only used when medical treatment is ineffective to relieve pressure on the median nerve, there are two methods: endoscopic and open surgery.
Prevention
- Change your working posture to avoid bad postures such as pressing on your wrists, sleeping on your hands, and taking care of and resting your hands properly to avoid putting pressure on the median nerve.
- Exercise your wrists correctly, at the correct range, and use a wrist brace.